What is General Aviation and Why is it Important for the Aviation Industry
General aviation plays a crucial role in the broader aviation industry, often overshadowed by commercial airliners but equally essential in fostering connectivity and economic growth. According to Dr. John B. Williams, an esteemed expert in aviation dynamics, "General aviation is the backbone of the aviation industry, providing access to remote areas and supporting various sectors." This highlights the significant contributions of general aviation to society, including emergency medical services, agricultural aviation, and business travel, thereby enhancing the overall functionality of the air transportation system.
As a diverse segment of aviation that encompasses all flights other than military and scheduled commercial airline flights, general aviation is vital for transport accessibility and local economies. The versatility of general aviation aircraft allows for unique applications ranging from aerial firefighting to flight training, illustrating its extensive utility. As we delve deeper into understanding what general aviation entails and why it holds importance within the industry, it becomes clear that this sector is not only about flying—it's about serving communities, supporting businesses, and ensuring that no place is too small to be connected.

Definition and Scope of General Aviation
General aviation refers to all civilian aviation operations other than scheduled air services and non-scheduled air transport services for remuneration or hire. This broad category includes a wide range of activities such as flight training, agricultural aviation, air charter services, medical transport, and recreational flying. General aviation encompasses everything from small single-engine airplanes used by private pilots to larger business jets, highlighting its diverse nature and the various roles it plays in the aviation ecosystem.
The scope of general aviation extends beyond mere transportation. It provides critical services such as emergency medical flights, which can save lives by delivering patients to hospitals quickly. Furthermore, general aviation supports industries by facilitating the transportation of goods and personnel to remote areas that may not be accessible by commercial airlines. Additionally, it serves as a vital training ground for future commercial pilots, ensuring a continuous supply of qualified professionals to meet the industry's demands. Overall, general aviation is an essential component of the aviation industry, contributing significantly to economic growth and connectivity on a local and national scale.
Historical Development of General Aviation
General aviation has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially, it emerged as a byproduct of the advancements in aeronautical engineering and the popularity of private flying. The first significant milestone occurred in the post-World War I period when surplus military aircraft became available to the public, allowing civilians to explore flying as a leisure activity. This era laid the groundwork for a burgeoning general aviation sector, supporting both recreational flying and a new business model focused on air transport and services.
As the decades progressed, advancements in technology and aircraft design further fueled the growth of general aviation. By the mid-20th century, more diverse aircraft options and the rise of flight schools transformed general aviation into a viable pathway for aspiring pilots. This development not only contributed to a growing number of licensed pilots but also created a robust support infrastructure, including maintenance facilities and air charter services. The historical trajectory of general aviation highlights its essential role in promoting accessibility, fostering innovation in flight technology, and enhancing rural connectivity, ultimately making it a critical component of the broader aviation industry.
Historical Development of General Aviation
General aviation has seen significant growth over the decades, particularly from the 1950s to the 2000s. This chart illustrates the number of registered general aviation aircraft in the United States, reflecting the increasing accessibility and importance of general aviation within the aviation industry.
Key Components and Types of General Aviation Aircraft
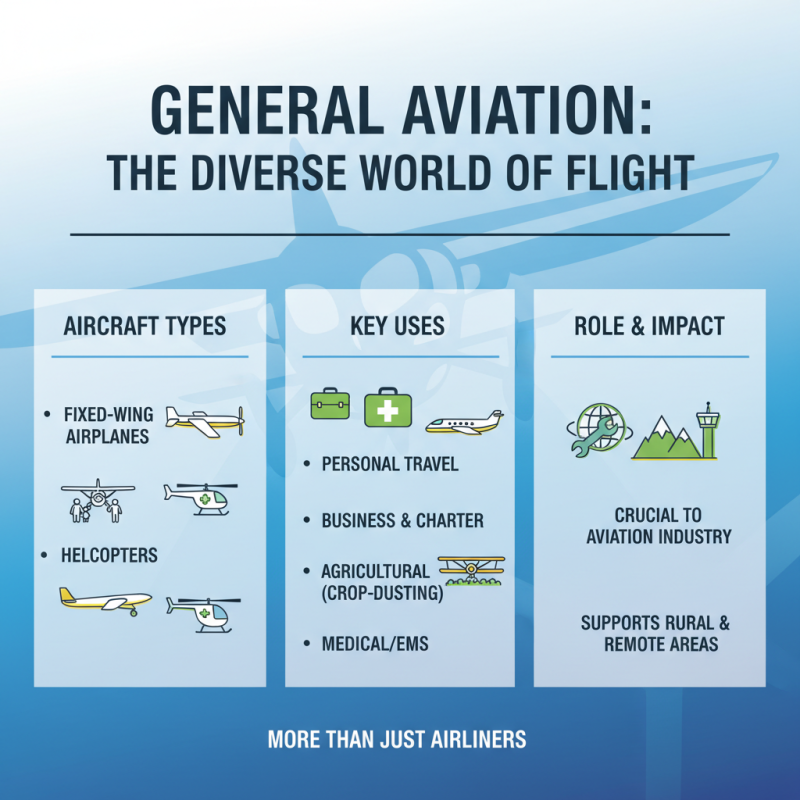
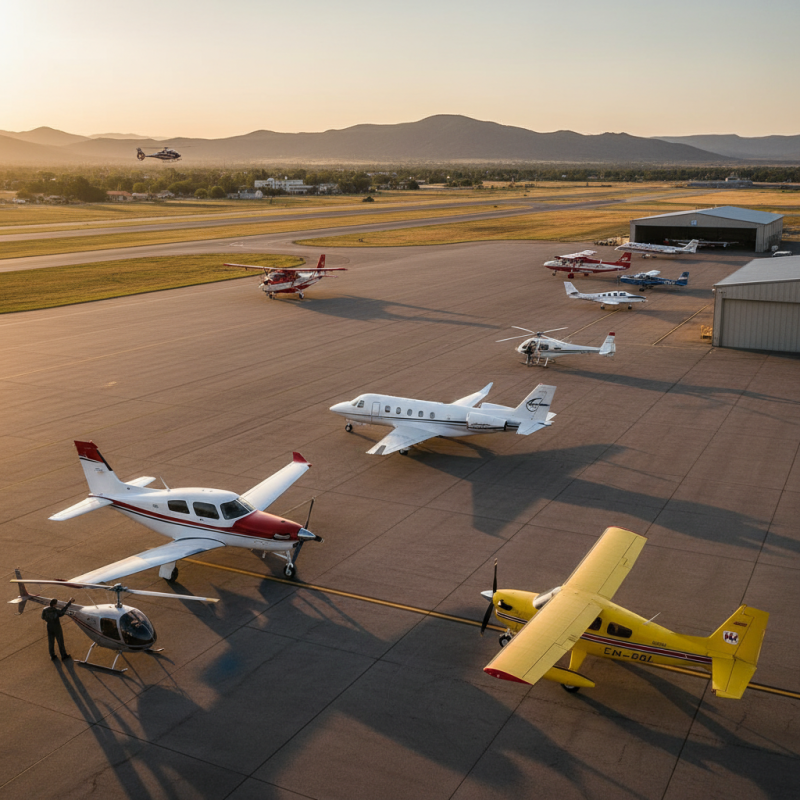
General aviation encompasses a diverse range of aircraft types and operations that play a crucial role in the aviation industry. Unlike commercial airliners, general aviation includes a variety of aircraft used for personal, business, agricultural, medical, and recreational purposes. This sector is characterized by both fixed-wing airplanes and helicopters, which serve a wide array of functions, from private flying to emergency medical services.
Key components of general aviation aircraft include single-engine and multi-engine planes, which are commonly used for flight training, private travel, and small-scale cargo transport. Helicopters, on the other hand, offer unique capabilities such as vertical takeoff and landing, making them invaluable for tasks like aerial surveys and search-and-rescue missions. Additionally, specialty aircraft, including seaplanes and business jets, cater to niche markets and contribute significantly to regional connectivity and economic activities. The versatility and accessibility of general aviation aircraft underscore their importance within the broader aviation ecosystem.
Economic Impact of General Aviation on Local Communities
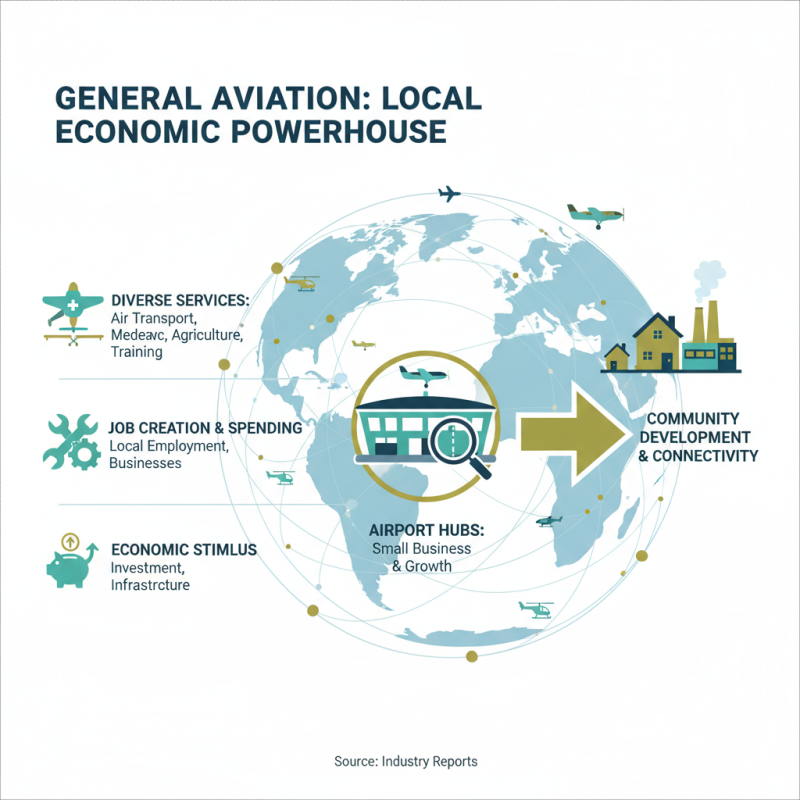
General aviation plays a crucial role in the economic landscape of local communities. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from private flying and flight training to emergency medical services and agricultural aviation. These services not only provide essential connectivity but also stimulate local economies by creating jobs and generating spending. Airports serve as hubs for small business operations, attracting investments that support local infrastructure and enhance community development.
Tips: Engage with your local general aviation community by attending events or joining flying clubs. This not only increases awareness of aviation’s economic benefits but also fosters relationships that can lead to mutually beneficial opportunities for local businesses and service providers.
Additionally, the presence of general aviation can boost tourism by facilitating easier access to remote areas. Travelers can reach destinations that are often overlooked by commercial airlines, bringing revenue to local hotels, restaurants, and attractions. This influx fosters a vibrant local economy, allowing communities to thrive and grow.
Tips: If you’re looking to support local tourism, consider exploring general aviation flight experiences. Connecting with local pilots might offer you unique sightseeing tours that highlight the beauty of your region from a different perspective.
Safety and Regulatory Framework in General Aviation
General aviation plays a crucial role in the aviation industry, providing a platform for a wide range of activities, including flight training, medical emergency services, and business transportation. Its safety and regulatory framework is essential for maintaining the integrity of all aviation operations. Unlike commercial aviation, general aviation encompasses a diverse array of aircraft and operators, making standardization and oversight particularly complex. Regulatory bodies focus on establishing comprehensive guidelines that cover pilot certification, aircraft maintenance, and operational procedures, ensuring a consistent approach to safety across the sector.
Tips for maintaining safety in general aviation include conducting regular aircraft maintenance checks, adhering strictly to pre-flight safety inspections, and ensuring pilots are well-trained and knowledgeable about the specific aircraft they operate. Additionally, having a thorough understanding of the relevant regulations and staying updated on any regulatory changes is crucial for all operators. Engaging with local aviation communities can also foster a culture of safety, where experiences and best practices are shared among pilots and operators.
Moreover, the regulatory framework also plays a vital role in risk management. By enforcing training standards and operational protocols, these regulations reduce the likelihood of accidents and enhance the reliability of general aviation services. Operators should embrace a proactive approach to compliance, ensuring that their practices align with the latest safety standards to protect both passengers and the broader aviation industry.
What is General Aviation and Why is it Important for the Aviation Industry - Safety and Regulatory Framework in General Aviation
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of General Aviation | Non-commercial aviation activities, including private flying, flight training, and aerial work. |
| Safety Regulations | The FAA and other regulatory bodies set safety standards and best practices. |
| Economic Impact | Contributes significantly to local economies through jobs and services. |
| Training and Certification | Pilots must obtain certifications tailored to specific aircraft types. |
| Community Benefits | General aviation facilitates medical evacuations, search and rescue, and disaster relief efforts. |
| Environmental Considerations | Efforts are being made to mitigate environmental impacts through technology and fuel improvements. |
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Future of Aviation: How Kit Aircraft are Redefining DIY Flight for Enthusiasts
-

10 Essential Tips for Beginners in General Aviation to Enhance Your Skills
-

Exploring the Future of Fuel System Aviation Innovations and Sustainability
-

Fuel Injection Aircraft Innovations Showcased at the 138th Canton Fair 2025
-

2025 Guide: How to Choose the Best Aircraft Service for Your Needs
-

Exploring the Future of Fuel Injection Aircraft: Innovations and Advancements in Aviation Technology
